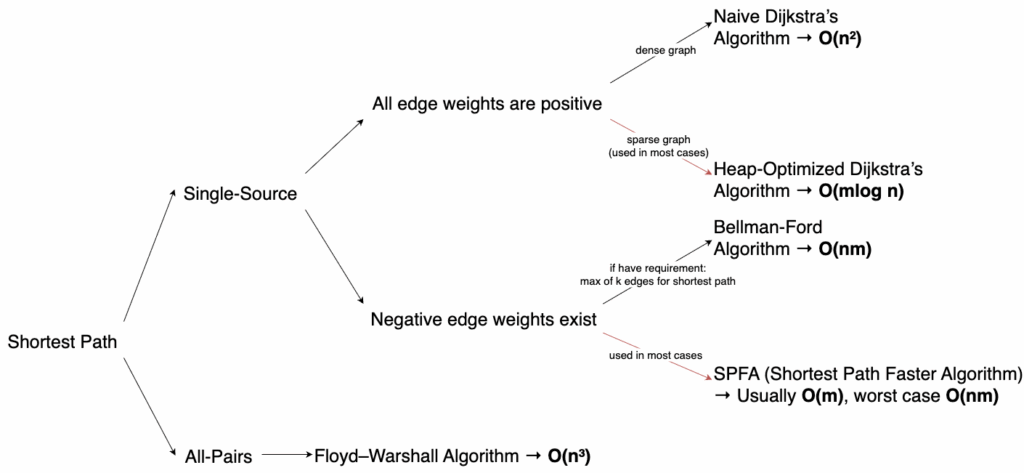
The following chart illustrates the decision flow for solving shortest path problems.
The Python templates for each algorithm are as follows:
Naive Dijkstra’s Algorithm – Used for Dense Graph
# n is number of nodes, g is the graph created
def dijkstra_naive_matrix(n, g):
dist = [INF] * (n + 1)
state = [False] * (n + 1) #record if a mininum dist confirmed or not
dist[1] = 0
for _ in range(n - 1):
t = -1 # find the node t with mininum dist
for j in range(1, n + 1):
if not state[j] and (t == -1 or dist[j] < dist[t]):
t = j
if t == -1: # rest nodes are unreachable
break
for j in range(1, n + 1):
if dist[j] > dist[t] + g[t][j]:
dist[j] = dist[t] + g[t][j]
state[t] = True
return -1 if dist[n] >= INF else dist[n]Heap-Optimized Dijkstra’s Algorithm – Used for Sparse Graph
# n is number of nodes, adj is the adjacency list created
def dijkstra_heap(n, adj):
dist = [INF] * (n + 1)
st = [False] * (n + 1)
dist[1] = 0
heap = [(0, 1)] # (distance, node)
while heap:
d, u = heapq.heappop(heap)
if st[u]:
continue
st[u] = True
for v, w in adj[u]:
if dist[v] > d + w:
dist[v] = d + w
heapq.heappush(heap, (dist[v], v))
return -1 if dist[n] >= INF else dist[n]Bellman-Ford Algorithm
INF = 10**9 # large sentinel for "infinity"
def bellman_ford(n, edges):
dist = [INF] * (n + 1)
dist[1] = 0
# Relax edges up to n - 1 times
for _ in range(n - 1):
updated = False
for a, b, w in edges:
if dist[a] < INF and dist[b] > dist[a] + w:
dist[b] = dist[a] + w
updated = True
# Optimization: stop early if no update
if not updated:
break
"""
# check one more time for negative cycle
for a, b, w in edges:
if dist[a] < INF and dist[b] > dist[a] + w:
return "negative cycle exist"
"""
# If still unreachable
if dist[n] > INF // 2:
return -1
return dist[n]SPFA
from collections import deque
INF = float('inf')
def spfa(n, adj):
dist = [INF] * (n + 1)
in_queue = [False] * (n + 1)
dist[1] = 0
q = deque([1])
in_queue[1] = True
while q:
u = q.popleft()
in_queue[u] = False
for v, w in adj[u]:
if dist[v] > dist[u] + w:
dist[v] = dist[u] + w
if not in_queue[v]:
q.append(v)
in_queue[v] = True
return -1 if dist[n] == INF else dist[n]Use SPFA to determine whether a graph contains a negative cycle
from collections import deque
INF = float('inf')
def has_negative_cycle(n, adj):
dist = [0] * (n + 1)
cnt = [0] * (n + 1)
q = deque()
for i in range(1, n + 1):
q.append(i)
in_queue = [True] * (n + 1)
while q:
u = q.popleft()
in_queue[u] = False
for v, w in adj[u]:
if dist[v] > dist[u] + w:
dist[v] = dist[u] + w
cnt[v] = cnt[u] + 1
# path to v uses >= n edges -> negative cycle reachable
if cnt[v] >= n:
return True
if not in_queue[v]:
q.append(v)
in_queue[v] = True
return FalseFloyd-Warshall Algorithm
INF = float('inf')
# initialize adj matrix
adj = [[INF] * (n + 1) for _ in range(n + 1)]
for i in range(1, n + 1):
adj[i][i] = 0
# adj[a][b] representing the shortest path between a and b
def floyd(n, adj):
for k in range(1, n + 1):
for i in range(1, n + 1):
for j in range(1, n + 1):
if adj[i][j] > adj[i][k] + adj[k][j]:
adj[i][j] = adj[i][k] + adj[k][j]
path[i][j] = path[k][j]